
A Linear Equation is a mathematical expression. It is an algebraic equation where one variable depends on other. It is generally appears in below form:
y = 6x + 2
The above equation is in the form of y = mx + b, where m and b are constant.
It is an equation that forms a straight line on a graph. In this particular equation, the constant m determines the slope or gradient of that line, and the constant term b determines the point at which the line crosses the y-axis, that is also known as the y-intercept. So, in the equation y = 6x + 2, slope m is 6 and y-intercept b is 2.
Linear equation is simple in manner and each term in linear equation will not have
- Exponents (or powers). For example, x2
- Multiplication or division of each other. For example: "x" times "y" or xy; "x" divided by "y" or x/y
- A root sign or square root sign (sqrt). For example: √x or the "square root x"; sqrt (x)
i) y = 2x+1 ii) 9x = 6+3y iii) y/4 = 9 - x
Linear equation will be in other form also. For example
i) y = 4 ii) 8x + 4 = 0 iii) y - 3 = ¼(x - 2)
The third example is in point-slope form [ y-y1 = m(x-x1) ]
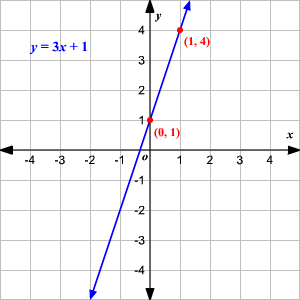
Linear equation graph
(Photo courtesy: hotmath.com)
Solving a linear equation:
i) 4x + 8 = 204x = 12
x = 12/4
x = 3
ii) ( (x-2)/3 ) + 1 = 2x/7
(x + 1)/3 = 2x/7
7 (x + 1) = 6x
7x +7 = 6x
7x - 6x = - 7
x = - 7


No comments:
Post a Comment